Class 12 Chemistry is a broad subject that requires a thorough understanding of the concepts and topics covered. As a result, we have provided Chemistry Notes PDF for IIT JEE/NEET to students and NEET aspirants. Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Notes PDF for NEET can be found below. With the help of detailed syllabus, Class 12 students learn what they need to study, how many points are assigned to each unit, and how much time is allotted for each unit. As a result, they can easily plan their study schedule.
Check out the Chemical Kinetics Class 12 notes PDF for your IIT JEE/NEET Preparation based on the IIT JEE/NEET Chemistry Syllabus. The Chemical Kinetics notes PDF is designed in such a way that it is very useful for IIT JEE/NEET aspirants.
CHEMICAL KINETICS
Deals with rate, mechanism and factors affecting the chemical reactions.
RATE OF REACTION
It is defined as the change in concentration of a reactant or a product in a particular interval of time. The change in concentration of a substance say A is represented by  [A]
[A]
 [A] = [Final concentration – Initial concentration]
[A] = [Final concentration – Initial concentration]
For a reactant : Final concentration < Initial concentration
Thus  [A] will have negative sign
[A] will have negative sign
For a product : Final concentration > Initial concentration
Thus  [A] will have positive sign
[A] will have positive sign
Average rate in terms of products = 
Average rate in terms of reactants = 
The negative sign in the expression make the rate positive.
Hence rate of a reaction is never negative.
Consider the decomposition of N2O5
Instantaneous rate of a reaction

Average rate of a reaction
The minus sign indicates the decrease in concentration and plus sign increase in concentration. The above expressions give the average rate of reaction.
FEATURES OF THE RATE OF REACTION
Rate of reaction is proportional to the concentration of the reactants
Rate of a reaction is always a positive quantity
Rate of a reaction is determined by measuring the concentration of a reactant or a product as a function of time
Property related to concentration is selected e.g. volume, pressure, thermal or electrical conductivity, colour change, pH, etc.
UNITS OF RATE OF REACTION
Mol L–1 time–1 and for gaseous reaction atm time–1
INSTANTANEOUS RATE
As the reaction progresses the concentration of reactants keeps on falling. Hence the rate of reaction keeps on falling with time. The rate of reaction at any given instant will be given by the expression
where dx is the infinitesimally small change in the concentration of x in infinitesimally small interval of time dt.
RELATION BETWEEN AVERAGE AND INSTANTANEOUS RATE
Instantaneous rate = Average rate as Dt approaches to zero
Instantaneous rate = 
FACTORS AFFECTING THE RATE OF REACTION
Nature of the reactants : Reactions involving lesser bond rearrangement proceed much faster than those which involve larger bond rearrangement.
Temperature : In most cases the rate of reaction in a homogeneous system is approximately doubled or even tripled by an increase in temperature of 10°C.
Concentration of reactants : At fixed temperature and in absence of catalyst, the rate increases with increased concentration of reactants.
Surface area : The more the surface area, the more is the rate of reaction.
Positive catalyst : Increases the rate by lowering the energy of activation.
Presence of light : Photochemical reactions are influenced by radiations of specific wavelength.
RATE CONSTANT
Consider a reaction A + B  Products
Products
At a particular temperature rate is given by
where k is rate constant, velocity constant or specific reaction rate.
When CA = CB = 1 then k= r (rate)
In general rate constant may be defined as the rate of the reaction when the concentration of each of the reactants is unity. It is characteristic of a particular reaction.
FACTORS INFLUENCING RATE CONSTANT
Variation of rate constant with temperature is given by
Arrhenius equation : k =  (i)
(i)
A = Constant known as frequency factor
Ea = Energy of activation. Both A and Ea are characteristic of a particular reaction.
 = known as Boltzmann factor
= known as Boltzmann factor
Taking natural logarithm of (i)
lnk =  (ii)
(ii)
The plot of lnk  gives a straight line
gives a straight line
Increase in temperature or decrease in the activation energy will increase the rate of reaction and exponential increase in the rate constant
At temperature T1 the equation (ii) is
lnk1 =  (iii)
(iii)
and at temperature T2
lnk2 = 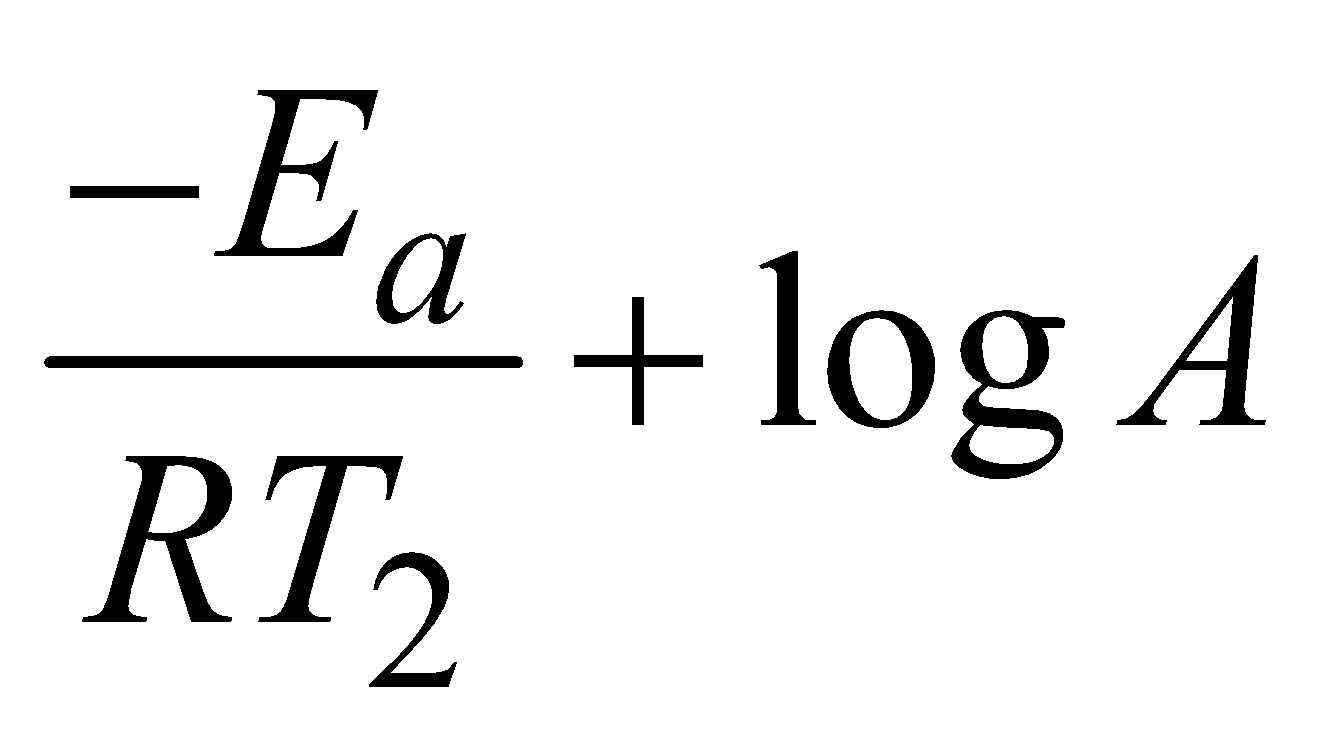 (iv)
(iv)
Since A is constant for a given reaction
Subtracting (iii) from (iv)
lnk2 – lnk1 = 
log = 
Knowing the value of slope Ea can be calculated.
UNITS OF RATE CONSTANT
Units depend upon the order of a reaction units = (Concentration)1 – n . time–1
= (Mol L–1)1–n . time–1
where n = order of reaction
Units of rate constant for zero order reaction = Mol L–1 time–1
Units of rate constant for first order reaction = time–1
CHARACTERISTICS OF RATE CONSTANT
The value of k is different for different reactions.
At fixed temperature the value of k is constant.
It is independent of concentration but depends on temperature.
The larger the value of k the faster is the reaction and vice versa.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN RATE CONSTANT AND RATE OF REACTION
TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENT
It is the ratio of two rate constants differing by a temperature of 10 °C. Generally the temperatures are 298K & 308 K.
Temperature Coefficient = 
The value of temperature coefficient is generally 2 and 3. In rare cases the value is 4, 5 etc.
RATE LAW EQUATION
The mathematical expression, which practically relates the rate of a chemical reaction and concentration of reactants is called rate law equation e.g. for a hypothetical reaction.
aA + bB  cC + dD
cC + dD
Rate  [A]a [B]b. It is law of mass action
[A]a [B]b. It is law of mass action
Rate  [A]x [B]y It is rate law.
[A]x [B]y It is rate law.
If rate actually vary according to this equation practically then this is rate law equation. For decomposition of N2O5.
2N2O5  2N2O4 + O2
2N2O4 + O2
 and not
and not 
Rate law equation is, Rate = k[N2O5]
Rate law equation for reversible reaction
Rate = [ Rate of forward reaction ] - [ Rate of backward reaction ]
Rate law equation involving side reactions
Rate of formation of 
Rate of formation of 
Rate = 
ORDER OF REACTION
The sum of all the powers to which the concentration terms are raised in rate law equation is known as the order of a reaction. For a general reaction
The rate law equation is
 ;
;
Order w.r.t. A is x,
Order w.r.t. B is y
Overall order is x + y
FEATURES OF ORDER OF REACTION
The order of a reaction is experimentally determined quantity.
It cannot be written from balanced chemical equation.
It can be written from the rate law equation.
It depends upon the molecules undergoing change in concentration.
Order may be zero, whole number, fractional or negative even
Reaction with order ≥ 3 are rare.
RATE DETERMINING STEP
Some reactions take place in more than one step. Each step has its own rate. The slowest step is called the rate determining step or rate controlling step e.g.
Mechanism 
First step is the rate determining step.
The rate law equation is always written from slow step.
∴ The rate law is given as
Remember that reaction intermediate are never shown in rate law equation.
MOLECULARITY OF REACTION
The number of molecules of reactants which take part in a single actual step of the reaction, whether their concentration is appreciably changed or not is known as molecularity of reaction. Molecularity is a theoretical concept and is always a whole number.
 Unimolecular
Unimolecular
 Bimolecular
Bimolecular
 Trimolecular
Trimolecular
The reactions with molecularity more than 3 are rare and generally not possible. Such reactions proceed through more than one steps and are termed as complex reactions. Each step has its own molecularity e.g.
Probable mechanism is
 Molecularity two
Molecularity two
 Molecularity two
Molecularity two
 Molecularity two
Molecularity two
 Molecularity five
Molecularity five
PSEUDO UNIMOLECULAR REACTIONS
Reactions like hydrolysis of an ester or cane sugar, which though bimolecular and yet following the kinetics of first order are called pseudo unimolecular reactions.
In above reactions the rate is independent of concentration of H2O being present in excess. Hence [H2O] is constant.
KINETIC EQUATIONS OF DIFFERENT ORDERS
FIRST ORDER REACTION
The reaction rate is determined by one concentration variable term.
A products
products
Let 'a' moles per unit volume be the initial concentration and x moles have disappeared after time t. Then the concentration left will be (a – x) moles per unit volume.
This is called the kinetic equation of a first order reaction.
Units of k = time–1 eg h–1, m–1 or s–1
Half-life period (t1/2) : The time taken for the completion of half of the reaction is known as half-life period. When  ,
,  .
.
The half-life period of the first order reaction is independent of the initial concentration of reacting substances.
Note : The time taken for the completion of any fraction of the reaction is independent of the initial concentration.
First order growth kinetics : It is used in population growth and bacteria multiplication
where a is initial population and (a + x) population after time t.
SECOND ORDER REACTION
The reaction rate is determined by the variation of two concentration terms. They are of two types
(a) 
(b) 
For the (a) type of reaction
Unit of k = conc–1 time–1 = (mol L–1)–1 time–1 i.e. mol–1 L. s–1
When ,  .
. 
Half-life period (t1/2) = 

The time taken for the completion of half of the reaction is inversely proportional to the initial concentration of the reactant.
Note: The time taken for the completion of half or any fraction of the reaction is inversely proportional to the initial concentration of the reactant.
THIRD ORDER REACTION
The reaction rate is determined by the variation of three concentration terms. They are of three types
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
Consider the type (a) k = 
Unit of k = (mol L–1)–2 s–1 = mol–2 L2 s–1
When t = t1/2, x = a/2
Half-life period (t1/2) =
The time taken for the completion of half of the reaction is inversely proportional to the square of the initial concentration of reactants.
Note : The time taken for the completion of any fraction of the reaction is inversely proportional to the square of the initial concentration of reactants.
ZERO ORDER REACTION
The reaction rate is independent of the concentration of the reactants.
Rate = k[A]0 or  on integration
on integration
x = kt + c
when t = 0, x = 0 so c = 0
Hence x = kt or k =
Unit of k = Conc. time–1 = mol L–1 s–1
When the reaction is complete, C = 0
For zero order reaction
Co = initial conc.
C = conc. at any time t
When 
Half life period (t1/2) = 
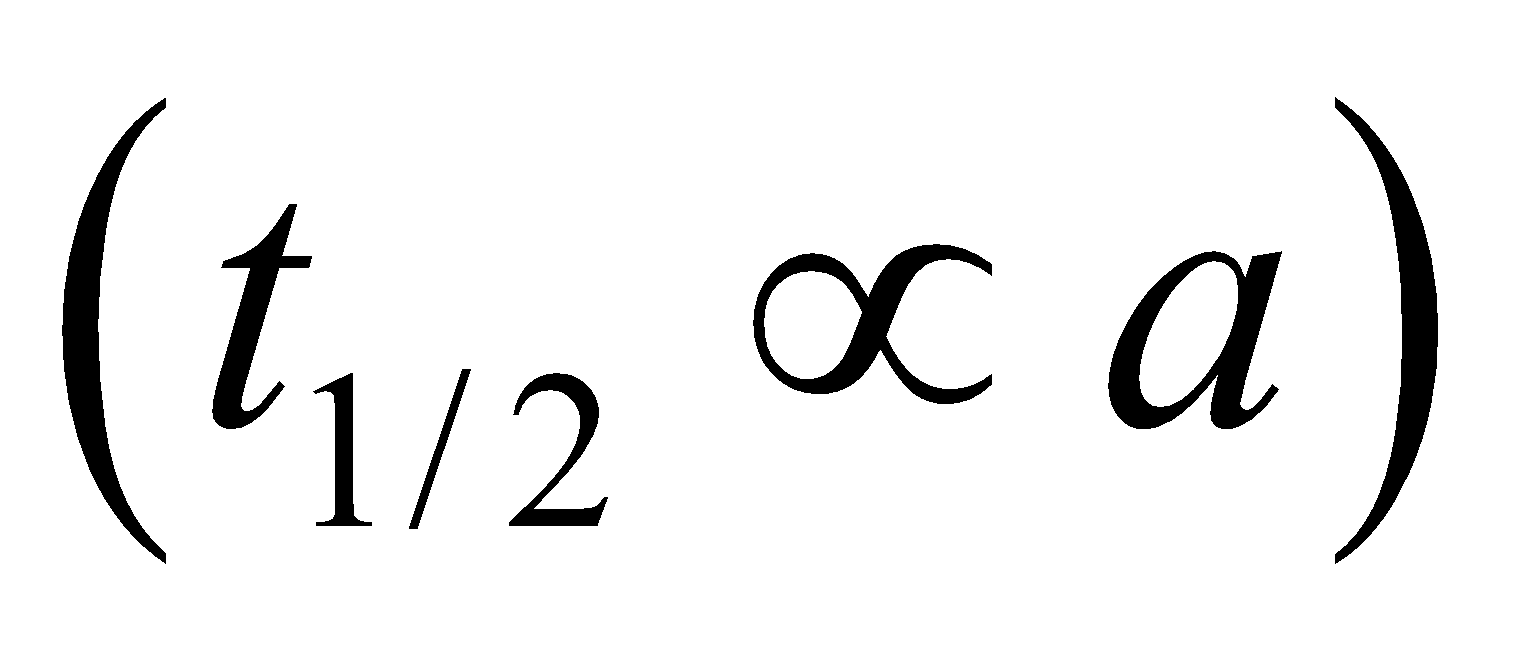
Note : The time taken for the completion of half of the reaction is directly proportional to the initial concentration of reactants.
For zero order reaction,
Rate is independent of concentration of reactant (s)
Concentration of reactants do not vary with time
Rate does not vary with time.
Rate is always equal to rate constant.
-
If we double the amount of reactants then time for completion will be doubled.
HALF-LIFE PERIOD FOR THE Nth ORDER REACTION
When the order of reaction is n, t1/2 is given by
Unit of k = (conc)1–n. time–1
FRACTIONAL ORDER REACTIONS
Rate = k PH2 (PD2)1/2. Order w.r.t. D2 is 1/2.
Order w.r.t. H2 is 3/2.
NEGATIVE ORDER REACTIONS
Conversion of ozone into oxygen.
Rate = K [O3]2 [O2]–1
Order with respect to oxygen is –1.
DETERMINATION OF ORDER OF REACTION
The time required to complete a definite fraction of reaction is given by
 where n is order of reaction
where n is order of reaction
The following graphs are obtained between t1/2 and initial concentration 'a'.
I.
II. 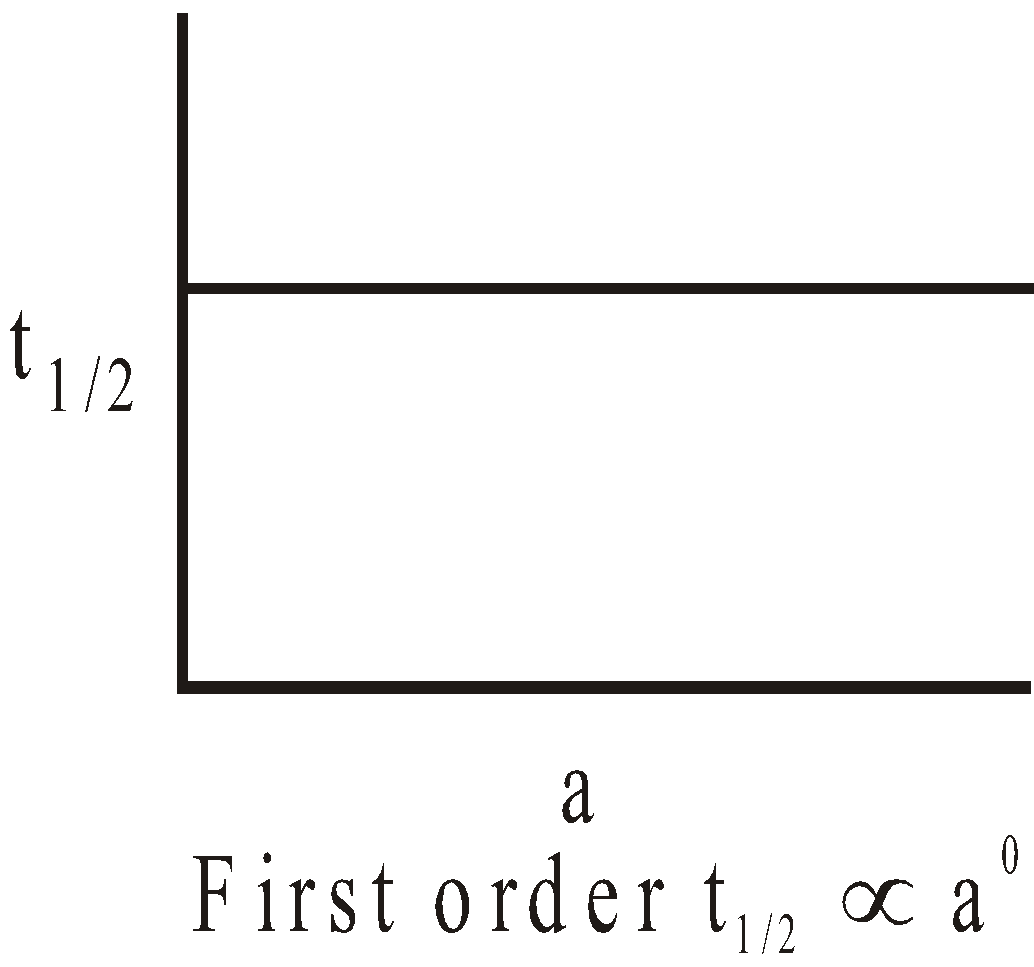
III. 
where n = 2 & 3
The graphs between concentration of any reactant Vs. time or concentration of any product Vs. time are plotted. The slope of the tangent to the curve gives the rate of reaction at that time.
The new graphs between  Vs. (a – x), (a – x)2 or (a – x)3 are plotted.
Vs. (a – x), (a – x)2 or (a – x)3 are plotted.
(b) Making use of integrated form of rate expression
Zero order 
Evaluation of k
For zero order slope = 
For I order slope =  ; k can be calculated
; k can be calculated
For II order slope = ; k can be calculated
; k can be calculated
For III order slope =  ; k can be calculated
; k can be calculated
Use of differential rate equations.
Use of integral rate equations – hit and trial method
Ostwald's isolation method.
EXAMPLES OF REACTIONS OF DIFFERENT ORDER
REACTIONS OF ZERO ORDER
REACTIONS OF IST ORDER
REACTIONS OF II ORDER
REACTIONS OF III ORDER
REACTIONS OF FRACTIONAL ORDER
REACTION OF IV ORDER
COLLISION THEORY
Chemical reaction occurs as a result of effective collisions between reacting molecules. For this two things are important.
THRESHOLD ENERGY
The minimum amount of energy possessed by the reacting molecules to have effective collisions, resulting in the formation of product, is called threshold energy.
ACTIVATION ENERGY (Ea)
The excess energy over and above the average potential energy possessed by reacting molecules to have effective collisions resulting in the formation of product is known as activation energy.
Activation Energy = threshold energy – average energy of reactants
For fast reaction the activation energy is low.
For slow reaction the activation energy is high.
COLLISION FREQUENCY (Z)
Total number of collisions which occur among the reacting molecules per second per unit volume is called collision frequency. Its value is given by
z = 
 = average velocity, s = molecular diameter in cm.,
= average velocity, s = molecular diameter in cm.,
n = number of molecules per cc.
RATE OF REACTION FROM COLLISION THEORY
It is given by
Rate of reaction = f × z
z = collision frequency, f = fraction of effective collisions
= 
Rate (k) = 
GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF EXOTHERMIC REACTION
where F.R. = Forward reaction and B.R. = Backward reaction
Graphical representation of endothermic reaction :
GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF THE EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON RATE OF REACTION
Fraction of the molecules having energy equal to activation energy is shown by shaded portion. The fraction of such molecules become almost double for 10°C rise of temperature and the rate of reaction almost doubles for 10°C rise of temperature.
PHOTOCHEMICAL REACTIONS
Reactions which take place by the absorption of radiations of suitable wavelength e.g.
Photosynthesis of carbohydrates in plants takes place in presence of chlorophyll and sunlight.
FREE ENERGY CHANGE IN PHOTOCHEMICAL REACTIONS
The free energy change of a photochemical reaction may not be negative. In the synthesis of carbohydrates and formation of HCl,  G is +ve.
G is +ve.
PHOTOSENSITISATION
Certain molecules absorb light energy and transfer it to another molecule which may undergo a reaction. The process is called photosensitisation and the substance doing so is called photosensitizer e.g. chlorophyll acts as photosensitizer in photosynthesis.
VISION
The isomerisation of retina by absorbing photon of light in the retina of eye and reconversion to original form by releasing energy is known as vision.
GROTTHUS-DRAPER LAW
Only those rays which are absorbed by the substance are effective in producing a chemical change. A part of light is reflected and transmitted also.
LAW OF PHOTOCHEMICAL EQUIVALENCE OR EINSTEIN'S LAW (STARK-EINSTEIN LAW)
In a photochemical reaction, one quantum of active light (photon) is absorbed per molecule of the reacting substance which disappears.
QUANTUM EFFICIENCY OR QUANTUM YIELD
Number of moles reacting per Einstein of the light absorbed. It is expressed as
CHEMILUMINESCENCE
Emission of light in a chemical reaction at ordinary temperature is called chemiluminescence.
FLUORESCENCE
The absorption of energy and instantaneous re-emitting of the energy is called fluorescence.
PHOSPHORESCENCE
The continuous glow of some substances even after the cutting of source of light is called phosphorescence e.g. ZnS.
BIOLUMINESCENCE
The phenomenon of chemiluminescence exhibited by certain living organisms is called bioluminescence e.g. light emission by fireflies.
EFFECT OF CATALYST ON REACTION RATES
A catalysed reaction provides a new pathway or a mechanism by which the potential energy barrier between the reactants and products is lowered. The graphical representation is as follows :
STUDY OF KINETICS OF SOME REACTIONS
HYDROLYSIS OF AN ESTER
CH3COOC2H5 + H2O  CH3COOH + C2H5OH
CH3COOH + C2H5OH
It is biomolecular and 1 order. The rate constant is given by
Initial conc. of ester  and conc. of ester present after time
and conc. of ester present after time .
.
INVERSION OF CANE SUGAR
The change is noted by rotation of plane polarised light in a polarimeter.
Hence velocity constant k is given by
SAPONIFICATION OF ETHYL ACETATE
Bimolecular II order reaction.
The value of k =
