Free Physics NEET Notes for Behavior Of Perfect Gas And Kinetic Theory
Free Physics Notes for Behavior Of Perfect Gas And Kinetic Theory (NEET)
Power up your NEET Exam prep with Chapter-Wise Physics Notes for Behavior Of Perfect Gas And Kinetic Theory at Onlineneetcoaching.in. Crafted by Brilliant Tutorial experts with 25 years of NEET insights.
- Behavior Of Perfect Gas And Kinetic Theory -
Important Physics Notes for IITJEE/NEET Preparation- Behavior Of Perfect Gas And Kinetic Theory
Class 11 Physics is a broad subject that requires a thorough understanding of the concepts and topics covered. As a result, we have provided Physics Notes PDF for IIT JEE/NEET to students and NEET aspirants. Behavior Of Perfect Gas And Kinetic Theory Class 11 Notes PDF for NEET can be found below. With the help of detailed syllabus, Class 11 students learn what they need to study, how many points are assigned to each unit, and how much time is allotted for each unit. As a result, they can easily plan their study schedule.
Check out the Behavior Of Perfect Gas And Kinetic Theory Class 11 notes PDF for your IIT JEE/NEET Preparation based on the IIT JEE/NEET Physics Syllabus. The Behavior Of Perfect Gas And Kinetic Theory notes PDF is designed in such a way that it is very useful for IIT JEE/NEET aspirants.
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
BEHAVIOUR OF GASES
IDEAL GAS
In an ideal gas, we assume that molecules are point masses and there is no mutual attraction between them. The ideal gas obeys following laws :
BOYLE’S LAW
According to Boyle’s law for a given mass of ideal gas, the pressure of a ideal gas is inversely proportional to the volume at constant temperature
i.e., 
CHARLE’S LAW
For a given mass, the volume of a ideal gas is proportional to temperature at a constant pressure
i.e., 
GAY-LUSSAC’S LAW
For a given mass of ideal gas, the pressure is proportional to temperature at constant volume
i.e., 
AVOGADRO’S LAW
According to Avogadro’s law, the number of molecules of all gases are same at same temperature, pressure and volume
i.e.,  for same P, V and T.
The value of Avogadro number is 6.02 × 1023 molecules.
for same P, V and T.
The value of Avogadro number is 6.02 × 1023 molecules.
GRAHAM’S LAW
-
At constant temperature and pressure, the rms speed of diffusion of two gases is inversely proportional to the square root of the relative density
i.e., vrms  ⇒
⇒
-
According to Graham’s law, the rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its density, provided pressure and temperature are constant

DALTON’S LAW
The pressure exerted by a gaseous mixture is equal to sum of partial pressure of each component gases present in the mixture,
i.e., P = P1 + P2 + P3+.................. Pn
A relation connecting macroscopic properties P, V and T of a gas describing the state of the system is called equation of state.
The equation of state for an ideal gas of n mole is
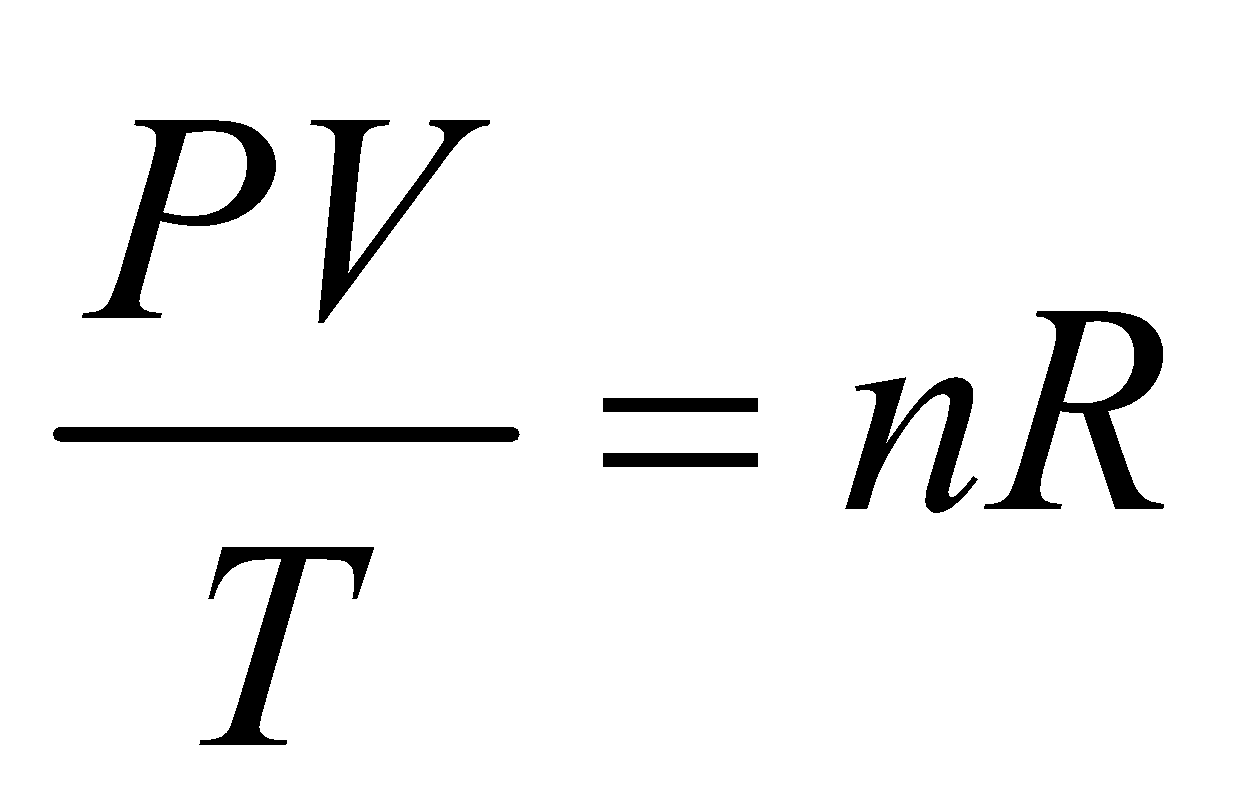 where R is universal gas constant whose value is
where R is universal gas constant whose value is
R = 8.31 J/mol K and R = NAk, where k is Boltzmann’s constant (NA is Avogadro number). n is the number of moles of a gas and
 , NA is Avogadro’s number
where m is the mass of a gas, N is the number of molecules and M is the molecular weight of a gas.
, NA is Avogadro’s number
where m is the mass of a gas, N is the number of molecules and M is the molecular weight of a gas.
EQUATION OF REAL GAS
The real gas follows Vander Wall’s law. According to this: ;
here a and b are Vander Waal’s constant

CRITICAL TEMPERATURE, VOLUME AND PRESSURE
-
The temperature at or below which a gas can be liquefied by applying pressure alone is called critical temperature TC. It is given by

-
The volume of gas at a critical temperature TC is called critical volume VC, where VC = 3b
-
The pressure of gas at a critical temperature TC is called critical pressure PC, where

GAS EQUATION
-
The gases found in nature are real gases.
-
The real gas do not obey ideal gas equation but they obey Vander Waal's gas equation

-
a' depends upon the intermolecular force and the nature of gas.
-
b' depends upon the size of the gas molecules and represents the volume occupied by the molecules of the gas.
-
The molecules of real gas have potential energy as well as kinetic energy.
-
The real gas can be liquefied and solidified.
-
The real gases like CO2, NH3, SO2 etc. obey Vander Wall's equn at high pressure and low temperature.
KINETIC THEORY OF AN IDEAL GAS
The basic assumptions of kinetic theory are :
-
A gas consist of particles called molecules which move randomly in all directions.
-
The volume of molecule is very small in comparison to the volume occupied by gas i.e., the size of molecule is infinitesimally small.
-
The collision between two molecules or between a molecule and wall are perfectly elastic and collision time (duration of collision) is very small.
-
The molecules exert no force on each other or on the walls of containers except during collision.
-
The total number of molecules are large and they obey Newtonian mechanics.
 ....(i)
where
....(i)
where  is called mean square velocity and
is called mean square velocity and  is called root mean square velocity
i.e,
is called root mean square velocity
i.e, 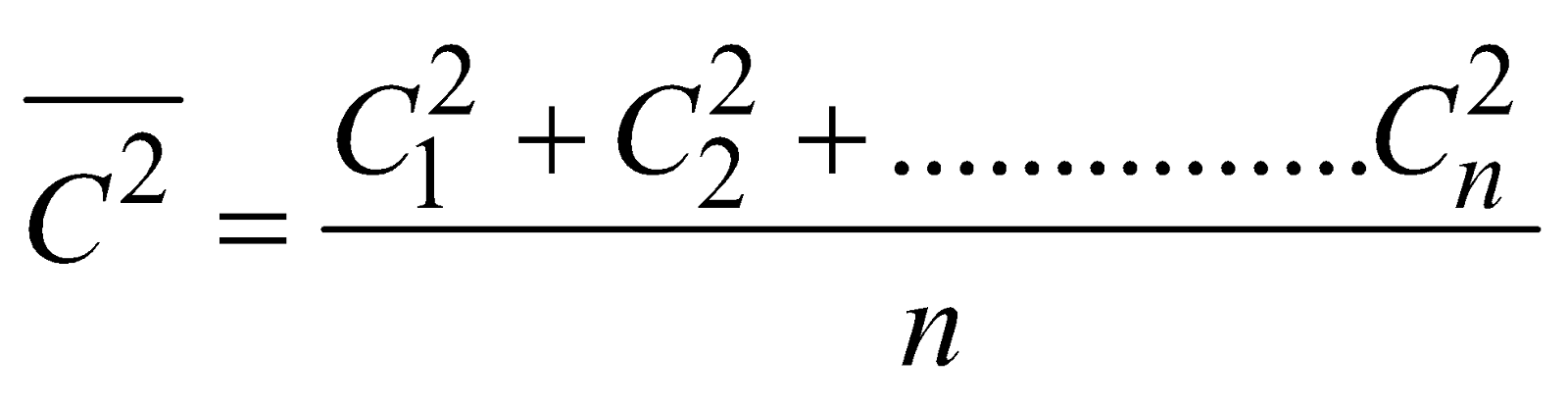 ....(ii)
and
....(ii)
and 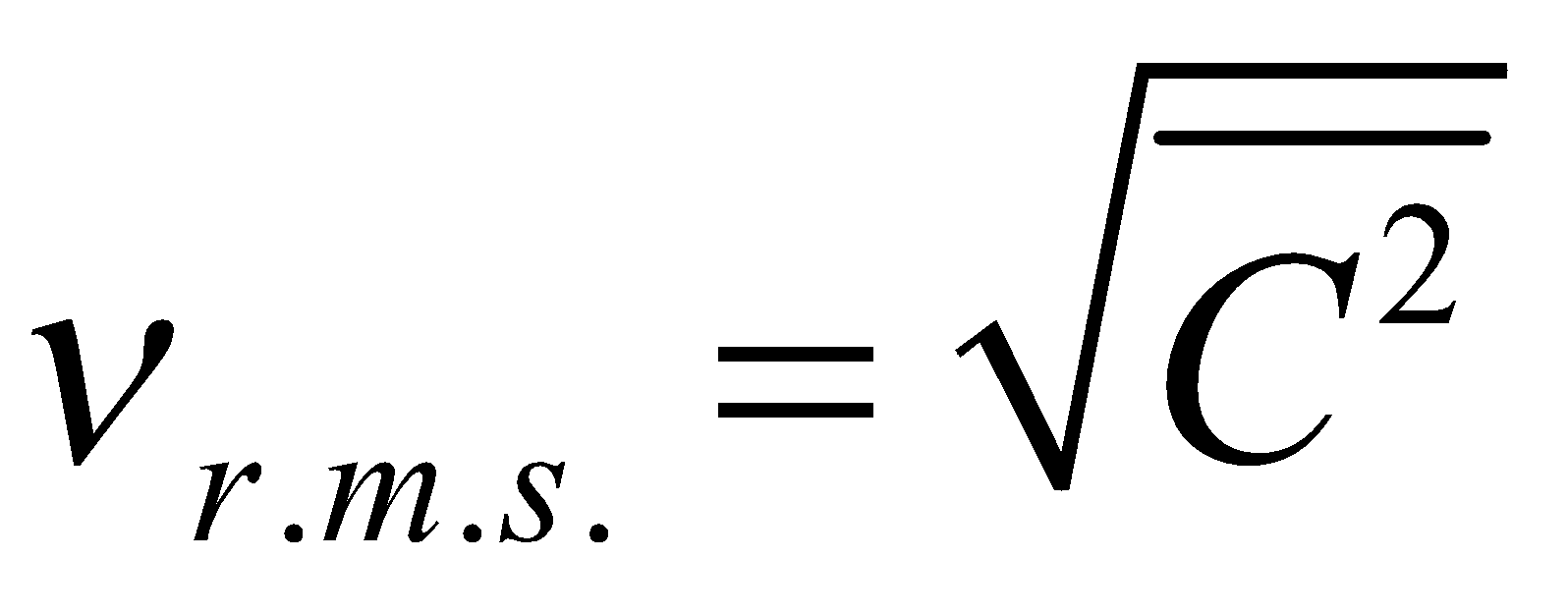 ....(iii)
where m = mass of one molecule and n = number of molecules
....(iii)
where m = mass of one molecule and n = number of molecules
 ....(iv)
or
....(iv)
or 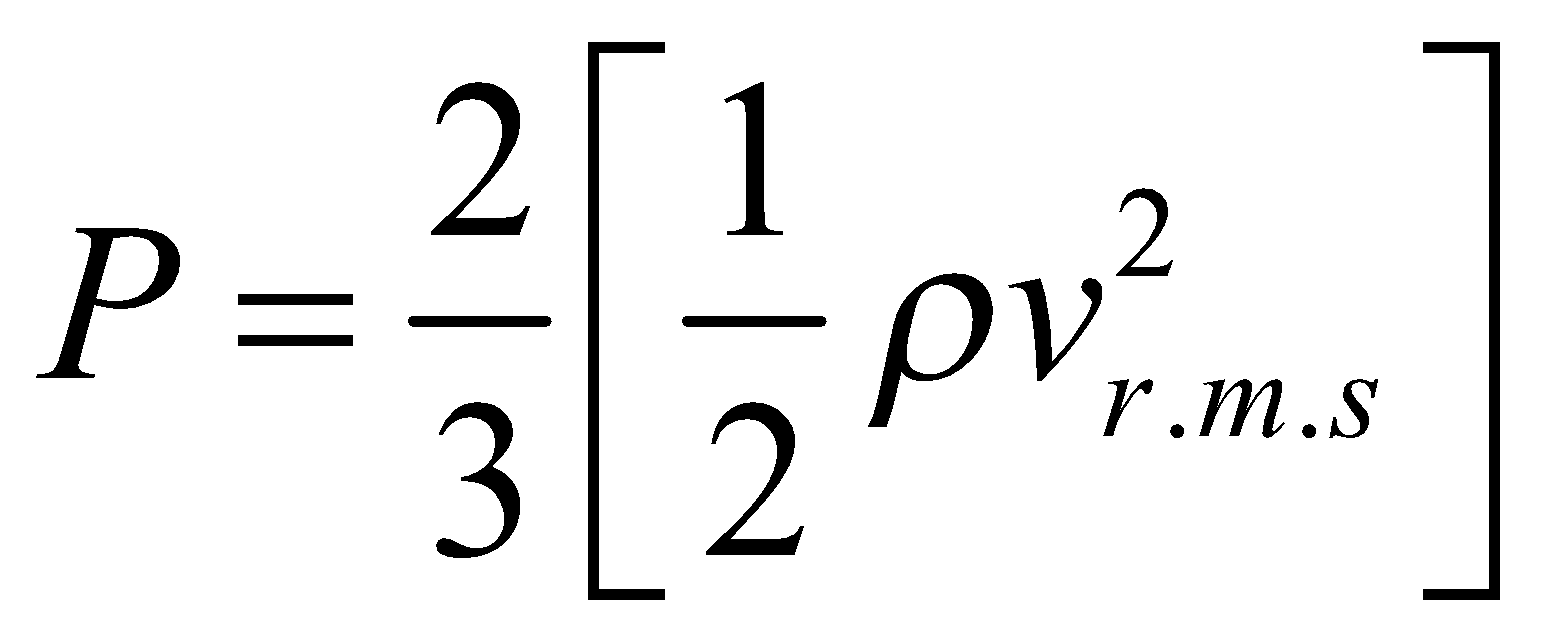
 or
or  ....(v)
where E is translational kinetic energy per unit volume of the gas. It is clear that pressure of ideal gas is equal to 2/3rd of translational kinetic energy per unit volume.
....(v)
where E is translational kinetic energy per unit volume of the gas. It is clear that pressure of ideal gas is equal to 2/3rd of translational kinetic energy per unit volume.
Kinetic interpretation of temperature : From eqn. (iv), we get
 For 1 mole of a gas at temperature T :
PV = RT so
For 1 mole of a gas at temperature T :
PV = RT so 
 (
( is Boltzmann constant)
or
is Boltzmann constant)
or  ....(vi)
or
....(vi)
or  or
or  ....(vii)
or
....(vii)
or 
It is clear from eq.(vi) that at a given temperature, the average translational kinetic energy of any gas molecules are equal i.e., it depends only on temperature.
From eqn. (vii) It is clear that
-
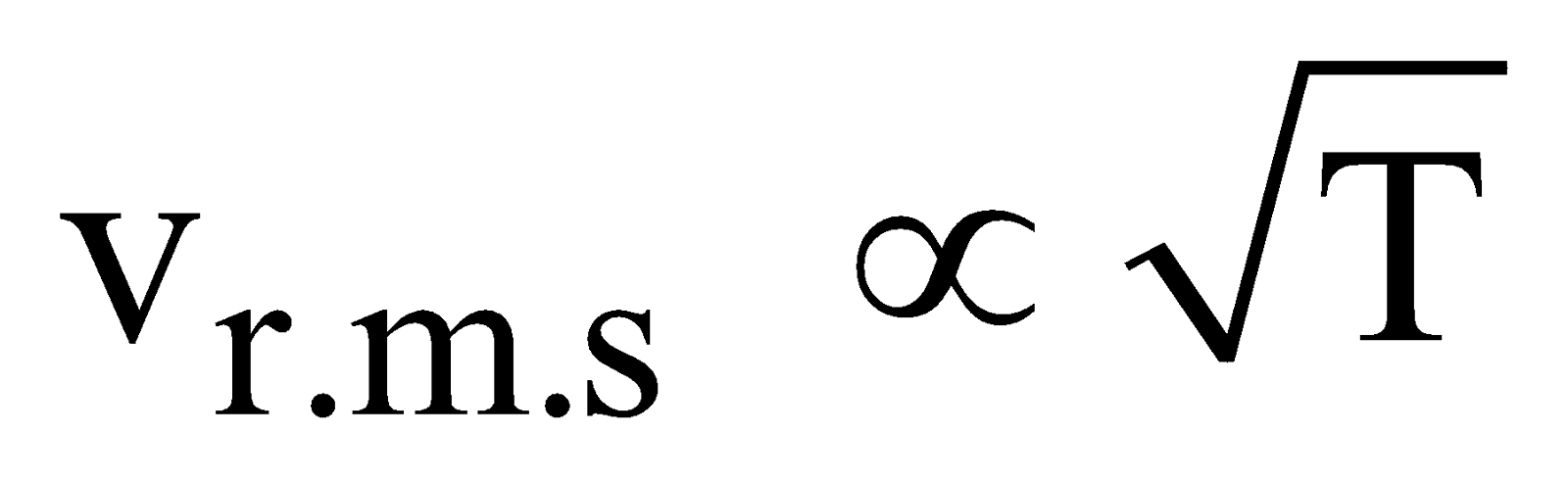
-
 , where M is molecular mass of the gas.
, where M is molecular mass of the gas.
DEGREE OF FREEDOM
The degree of freedom of a particle is the number of independent modes of exchanging energy or the number of independent motion, which the particle can undergo.
For monatomic gas such as helium, argon, neon etc. the molecules can have three independent motion i.e., it has
3 degree of freedom, all translational.
 For a diatomic gas molecules such as H2, O2, N2, etc. it has two independent rotational motion besides of three independent translational motion, so it has 5 degree of freedom.
For a diatomic gas molecules such as H2, O2, N2, etc. it has two independent rotational motion besides of three independent translational motion, so it has 5 degree of freedom.
 In polyatomic gas molecules such as CO2, it can rotate about any of three coordinate axes. It has six degree (three translational + three rotational) of freedom. At high temperature the molecule can vibrate also and degree of freedom due to vibration also arises, but we neglect it.
In polyatomic gas molecules such as CO2, it can rotate about any of three coordinate axes. It has six degree (three translational + three rotational) of freedom. At high temperature the molecule can vibrate also and degree of freedom due to vibration also arises, but we neglect it.
MEAN FREE PATH
The distance covered by the molecules between two successive collisions is called the free path.
The average distance covered by the molecules between two successive collisions is called the mean free path.
i.e., 
 where, n = number of molecules per unit volume
d = diameter of each molecule
KB = Boltzmann’s constant
T = temperature
P = pressure
Mean free path depends on the diameter of molecule (d) and the number of molecules per unit volume n.
At N.T.P., λ for air molecules is 0.01 µm.
where, n = number of molecules per unit volume
d = diameter of each molecule
KB = Boltzmann’s constant
T = temperature
P = pressure
Mean free path depends on the diameter of molecule (d) and the number of molecules per unit volume n.
At N.T.P., λ for air molecules is 0.01 µm.
LAW OF EQUIPARTITION OF ENERGY
If we dealing with a large number of particles in thermal equilibrium to which we can apply Newtonian mechanics, the energy associated with each degree of freedom has the same average value (i.e., ), and this average value depends on temperature.
From the kinetic theory of monatomic ideal gas, we have
), and this average value depends on temperature.
From the kinetic theory of monatomic ideal gas, we have
 ....(i)
or
Energy of molecule = (number of degree of freedom) ×
....(i)
or
Energy of molecule = (number of degree of freedom) ×  ....(ii)
So it is clear from equation (i) and (ii) that monatomic gas has three degree of freedom and energy associated per degree of freedom is
....(ii)
So it is clear from equation (i) and (ii) that monatomic gas has three degree of freedom and energy associated per degree of freedom is  (where k is Boltzmann’s constant)
(where k is Boltzmann’s constant)
Since we know that internal energy of an ideal gas depends only on temperature and it is purely kinetic energy. Let us consider an 1 mole ideal gas, which has N molecules and f degree of freedom, then total internal energy
U = (total number of molecules)
× (degree of freedom of one molecule)
× (energy associated with each degree of freedom)
=(N) (f) × (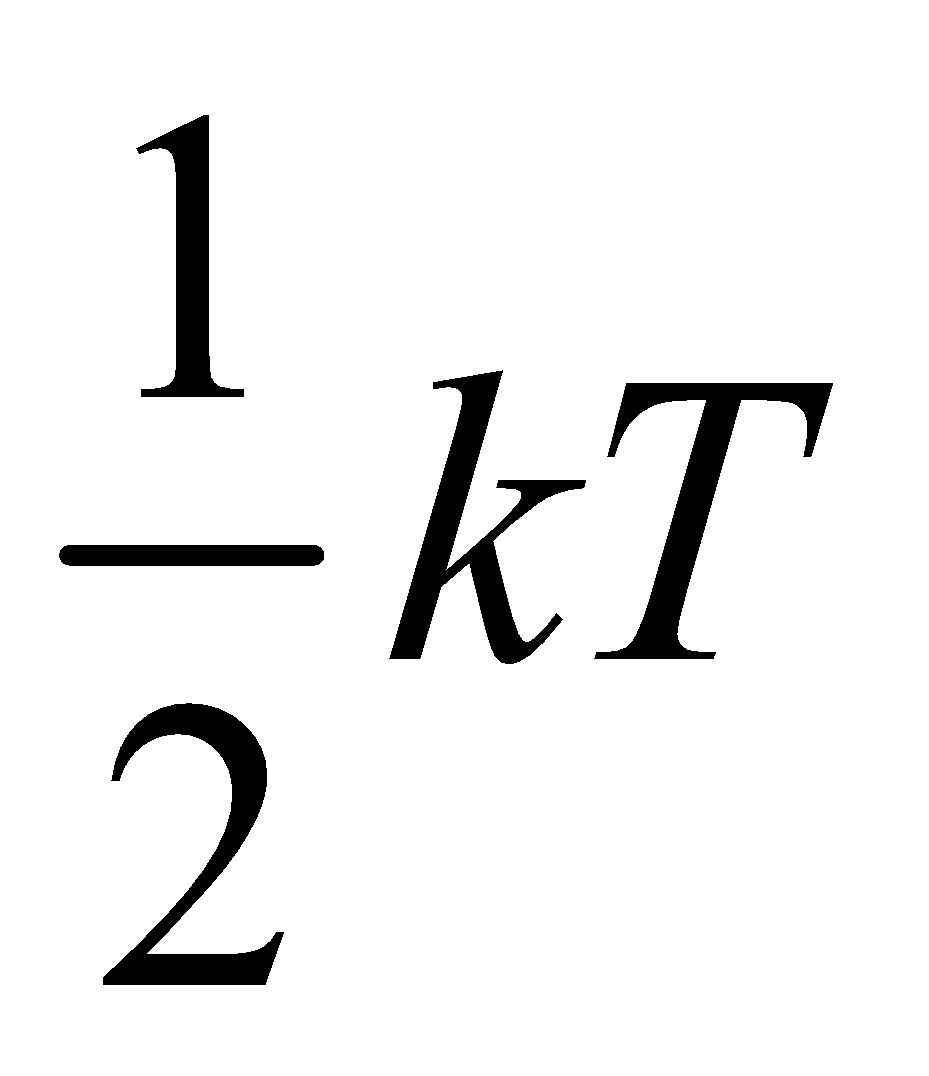 )
U = Nf
)
U = Nf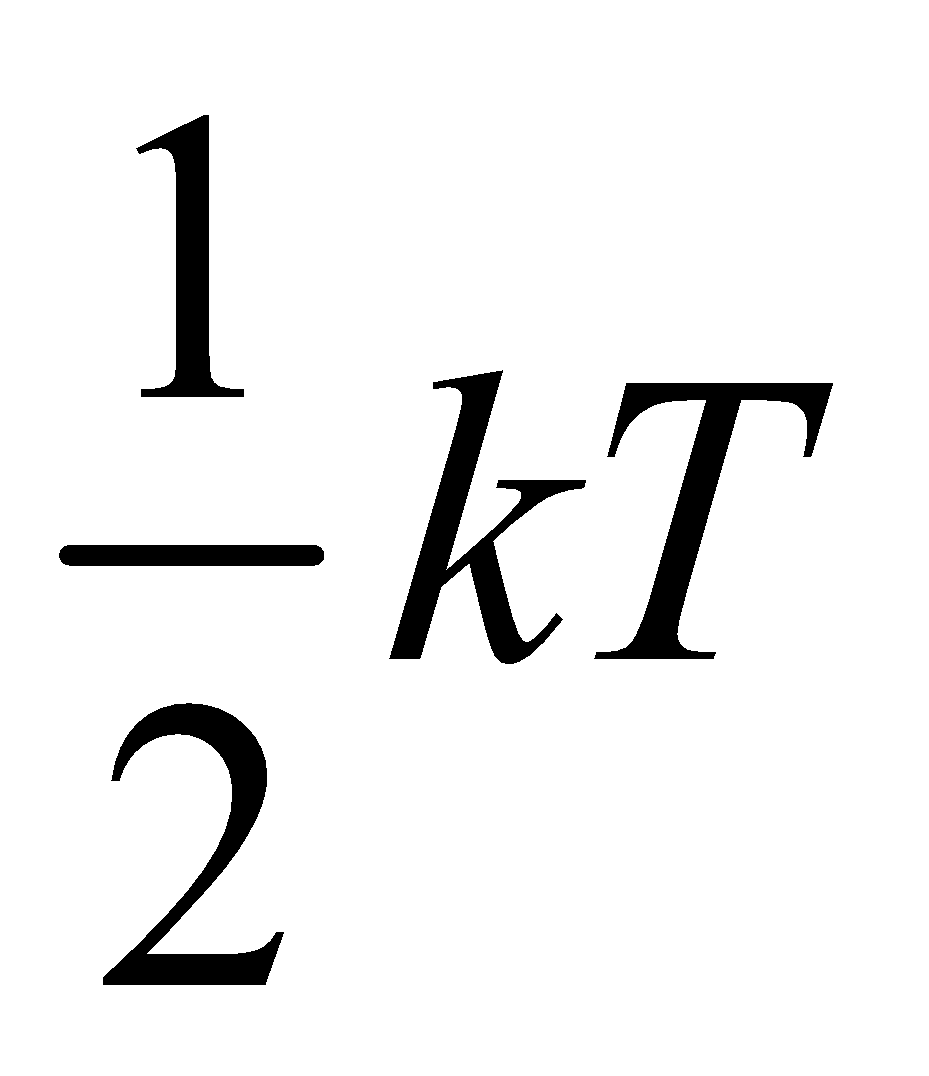 ....(iii)
Differentiating eq.(iii) w.r.t T, at constant volume, we get,
....(iii)
Differentiating eq.(iii) w.r.t T, at constant volume, we get,
 ....(iv)
Now molar, specific heat at constant volume is defined as
....(iv)
Now molar, specific heat at constant volume is defined as
 ....(v)
so
....(v)
so 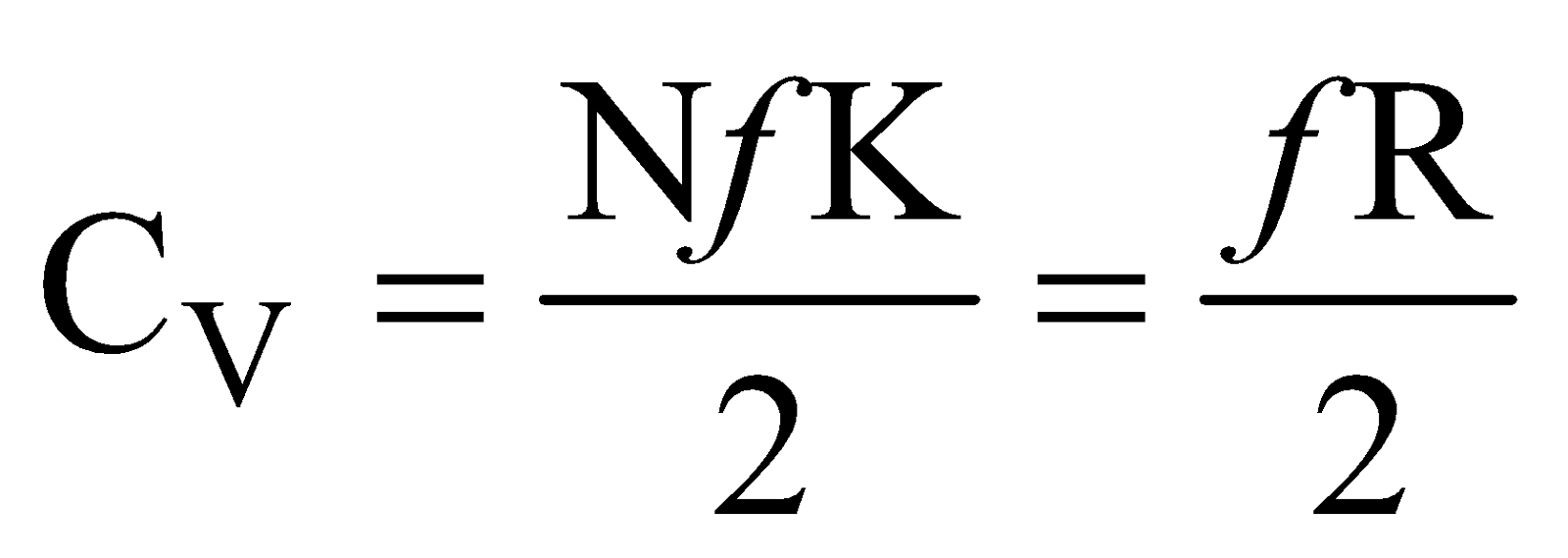 ....(vi)
where R is universal gas constant.
Now by Mayer’s formula,
....(vi)
where R is universal gas constant.
Now by Mayer’s formula,
 …. (vii)
So ratio of specific heat
…. (vii)
So ratio of specific heat  is
is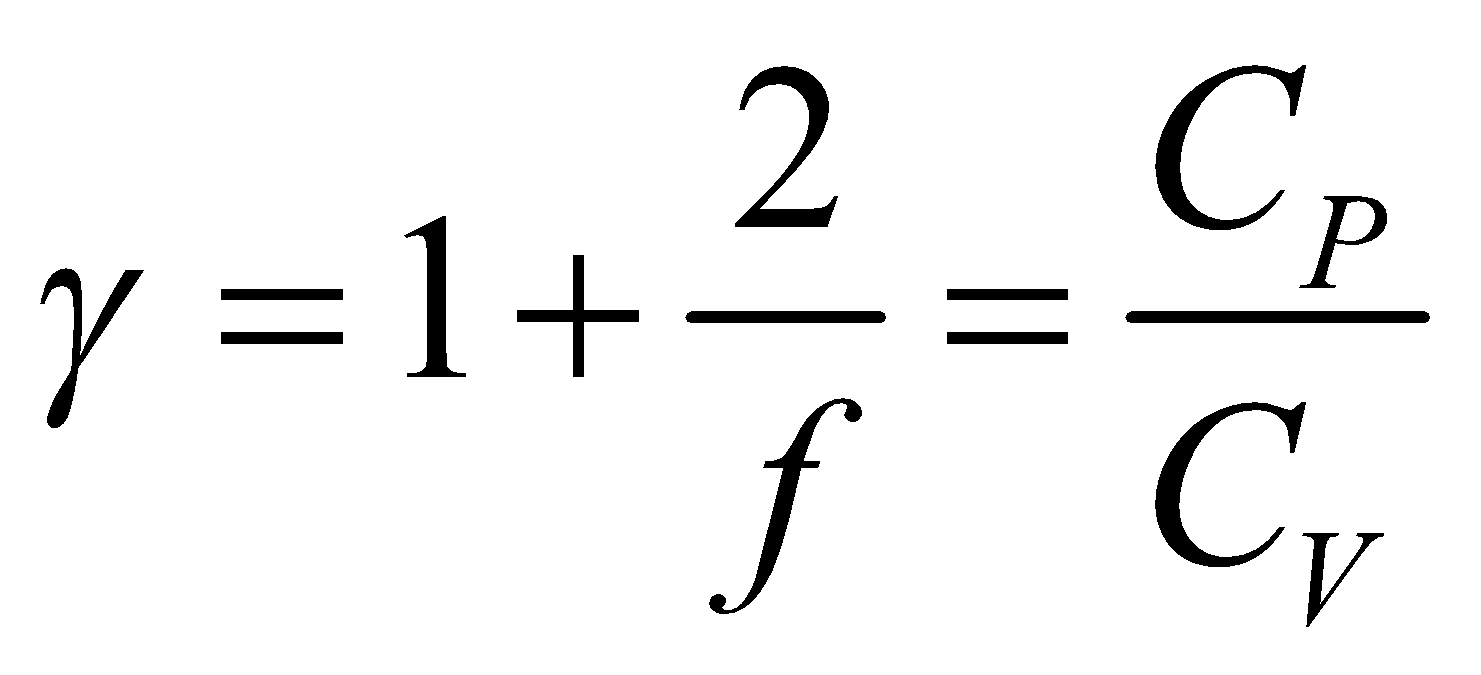 ...(viii)
where f is degree of freedom of one molecule.
(a) For monatomic gas, f = 3,
...(viii)
where f is degree of freedom of one molecule.
(a) For monatomic gas, f = 3,  ,
, so
so  (b) For diatomic gas, f = 5,
(b) For diatomic gas, f = 5,  ,
, 
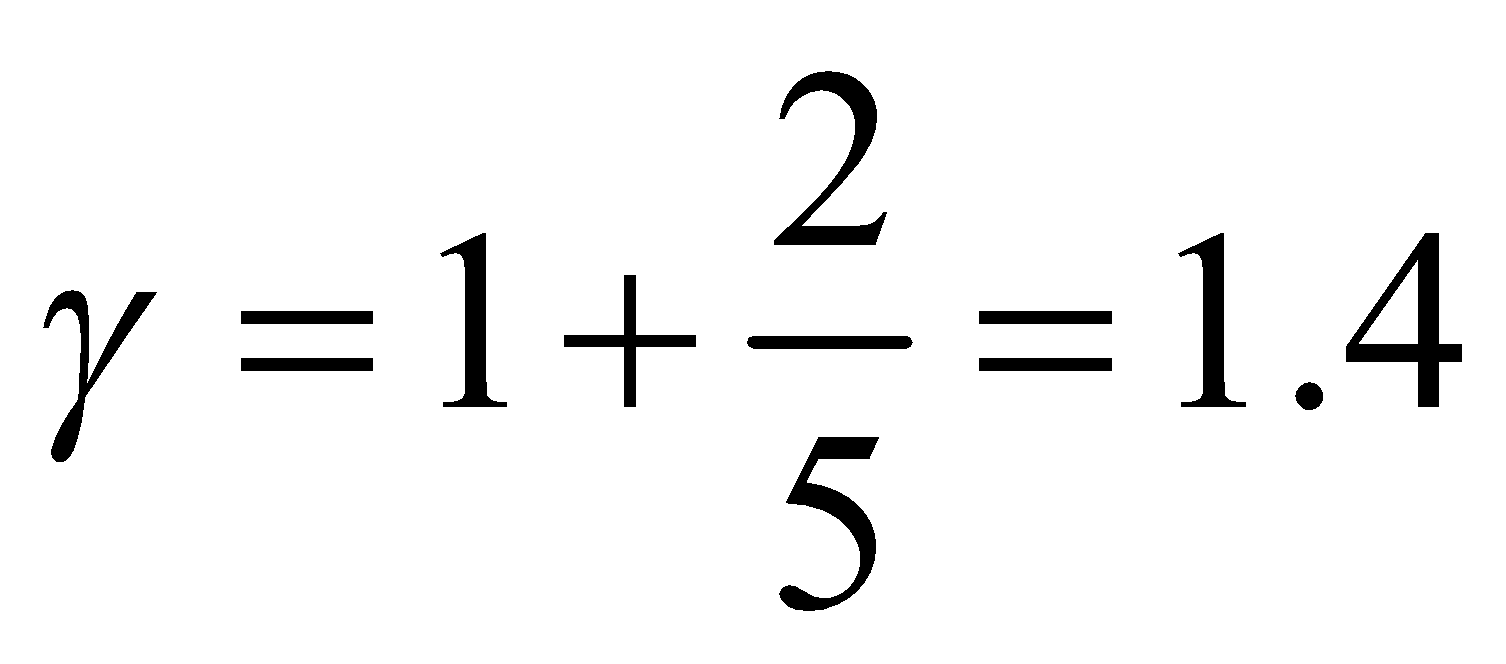 (c) For polyatomic gas, f = 6,
(c) For polyatomic gas, f = 6,  ,
, 

KEEP IN MEMORY
-
Real gases behave like perfect gas at high temperature and low pressure.
In real gas, we assume that the molecules have finite size and intermolecular attraction acts between them.
-
Real gases deviate most from the perfect gas at high pressure and low temperature.
-
Gaseous state of matter below critical temperature is called vapours. Below critical temperature gas is vapour and above critical temperature vapour is gas.
-
Random motion of the constituents of the system involving exchange of energy due to mutual collisions is called thermal motion.
-
Total kinetic energy or internal energy or total energy does not depend on the direction of flow of heat. It is determined by the temperature alone.
-
The internal energy of a perfect gas consists only of kinetic energy of the molecules. But in case of the real gas it consists of both the kinetic energy and potential energy of inter molecular configuration.
DISTRIBUTION OF MOLECULAR SPEEDS
The speed of all molecules in a gas is not same but speeds of individual molecules vary over a wide range of magnitude.
Maxwell derived the molecular distribution law (by which we can find distribution of molecules in different speeds) for sample of a gas containing N molecules, which is
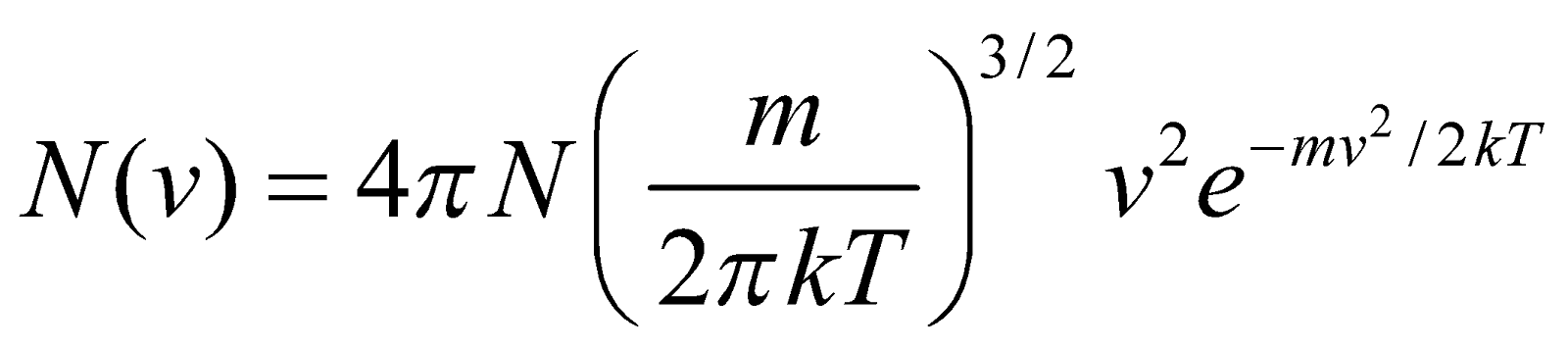 ...(1)
where N(v)dv is the number of molecules in the gas sample having speeds between v and v + dv.
where T = absolute temperature of the gas
m = mass of molecule
k = Boltzmann’s constant
The total number of molecules N in the gas can be find out by integrating equation (1) from 0 to ∞ i.e.,
...(1)
where N(v)dv is the number of molecules in the gas sample having speeds between v and v + dv.
where T = absolute temperature of the gas
m = mass of molecule
k = Boltzmann’s constant
The total number of molecules N in the gas can be find out by integrating equation (1) from 0 to ∞ i.e.,
 ....(2)
....(2)
 Figure shows Maxwell distribution law for molecules at two different temperature T1 and T2(T2 > T1).
The number of molecules between v1 and v2 equals the area under the curve between the vertical lines at v1 and v2 and the total number of molecules as given by equation (2) is equal to area under the distribution curve.
The distribution curve is not symmetrical about most probable speed, vP,(vP is the speed, which is possessed in a gas by a large number of molecules) because the lowest speed must be zero, whereas there is no limit to the upper speed a molecule can attain. It is clear from fig.1 that
vrms(root mean square) >
Figure shows Maxwell distribution law for molecules at two different temperature T1 and T2(T2 > T1).
The number of molecules between v1 and v2 equals the area under the curve between the vertical lines at v1 and v2 and the total number of molecules as given by equation (2) is equal to area under the distribution curve.
The distribution curve is not symmetrical about most probable speed, vP,(vP is the speed, which is possessed in a gas by a large number of molecules) because the lowest speed must be zero, whereas there is no limit to the upper speed a molecule can attain. It is clear from fig.1 that
vrms(root mean square) > 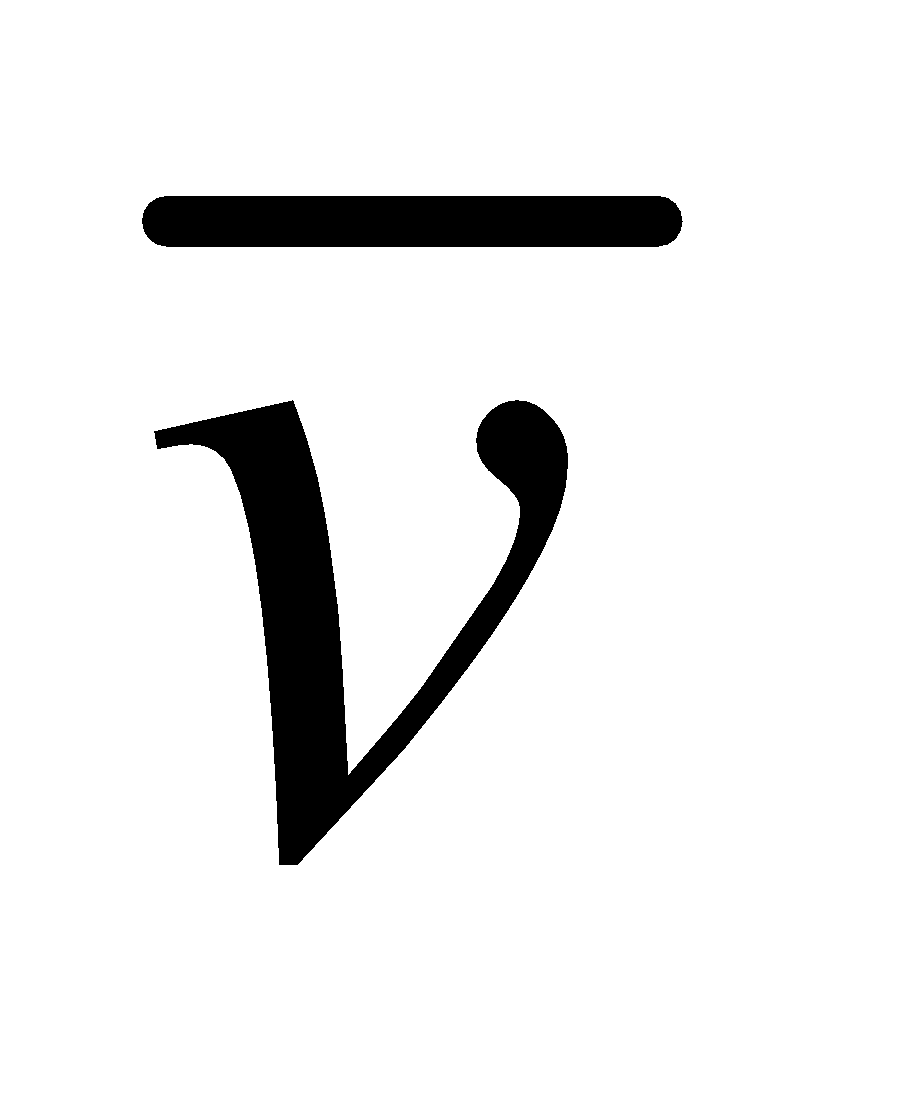 (average speed of molecules) > (most probable speed) vP
(average speed of molecules) > (most probable speed) vP
AVERAGE, ROOT MEAN SQUARE AND MOST PROBABLE SPEED
AVERAGE SPEED
To find the average speed  , we multiply the number of particles in each speed interval by speed v characteristic of that interval. We sum these products over all speed intervals and divide by total number of particles
i.e.,
, we multiply the number of particles in each speed interval by speed v characteristic of that interval. We sum these products over all speed intervals and divide by total number of particles
i.e.,  (where summation is replaced by integration because N is large)
(where summation is replaced by integration because N is large)
 ....(1)
....(1)
ROOT MEAN SQUARE SPEED
In this case we multiply the number of particles in each speed interval by v2 characteristic of that interval; sum of these products over all speed interval and divide by N
i.e.,  ....(2)
Root mean square speed is defined as
....(2)
Root mean square speed is defined as

MOST PROBABLE SPEED
It is the speed at which N(v) has its maximum value (or possessed by large number of molecules), so
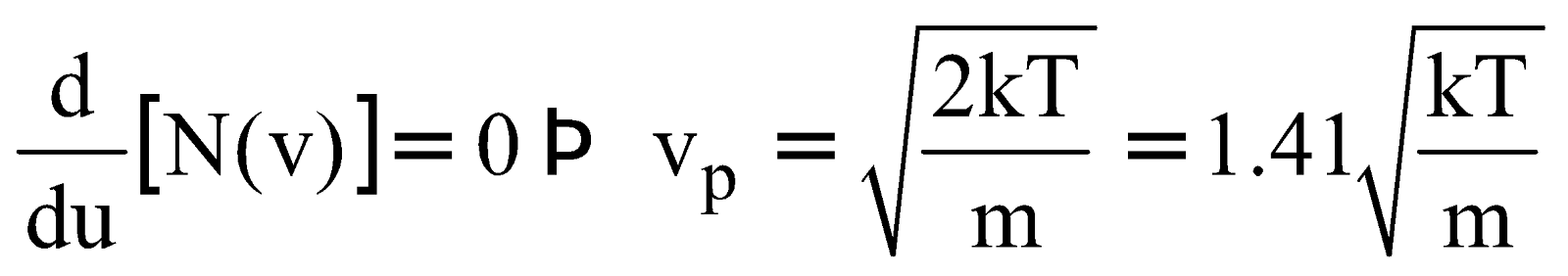 ....(3)
It is clear from eqn. (1), (2) and (3)
....(3)
It is clear from eqn. (1), (2) and (3)
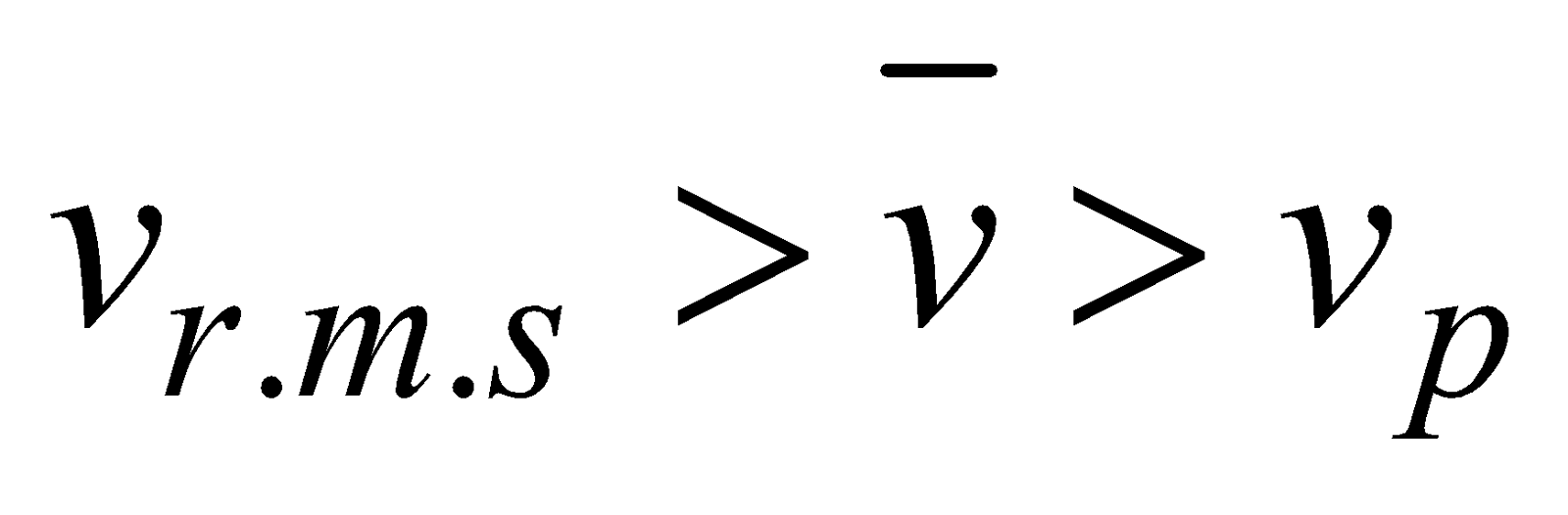 The root mean square velocity of a particle in thermal system is given by
The root mean square velocity of a particle in thermal system is given by
 where R - universal gas constant
T - temperature of gas
m - mass of the gas
M - molecular weight of gas or mass of one mole of a gas.
The average speed of the gas molecules is given by
where R - universal gas constant
T - temperature of gas
m - mass of the gas
M - molecular weight of gas or mass of one mole of a gas.
The average speed of the gas molecules is given by
 where M is the mass of one mole and m is the mass of one particle.
Most probable speed is that with which the maximum number of molecules move. It is given by
where M is the mass of one mole and m is the mass of one particle.
Most probable speed is that with which the maximum number of molecules move. It is given by
 The most probable speed, the average speed as well as root mean square speed increases with temperature.
The most probable speed, the average speed as well as root mean square speed increases with temperature.
KEEP IN MEMORY
-
Brownian motion, provides a direct evidence for the existence of molecules and their motion. The zig-zag motion of gas molecules is Brownian motion.
-
Average speed

-
Root mean square speed,

-
Most probable speed

-
Vrms :
 : Vmp = 1.73 : 1.60 : 1.41
: Vmp = 1.73 : 1.60 : 1.41
Vrms >  > Vmp.
> Vmp.
R = 8.31 J/mol K and R = NAk, where k is Boltzmann’s constant (NA is Avogadro number). n is the number of moles of a gas and
- a' depends upon the intermolecular force and the nature of gas.
- b' depends upon the size of the gas molecules and represents the volume occupied by the molecules of the gas.
3 degree of freedom, all translational.
